POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME (PCOS)

The syndrome of polycystic ovary (PCOS) is a complicated and hormonal problem that affects women of reproductive age. Signs and symptoms may significantly differ among individuals; hence it is different in every case. The three core features for diagnosing PCOS are irregular menstrual cycles, excessive levels of androgens (which leads to acne, growing hair on unusual parts of the body, or baldness), and polycystic ovaries, as shown by ultrasound examination. However, not all women with PCOS will have all these symptoms, nor will this syndrome always present in the same way.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) patients at Grace Women’s Hospital receive specialized care. It provides personalized treatment plans targeting various signs and complications associated with the disease.
Upon admission at Grace Women’s Hospital, PCOS patients are given a thorough investigation, including taking a good medical history, physical examination, as well as advanced diagnostic tests so as to accurately diagnose the condition and its attendant morbidity. Additionally, the hospital uses ultrasonography; here, the ovaries are checked out for cysts, and blood samples are taken for hormonal studies along with insulin resistance investigations.
In addition to being a reproductive disorder, PCOS can have metabolic implications; thus, our facility offers a multidisciplinary approach to management. These include lifestyle changes such as weight reduction measures and improving insulin sensitivity through dieting counseling aside from medications, which help regulate the menstrual cycle whilst lowering excess masculine hormones, plus fertility promotion procedures for those who wish to be pregnant. For example, girls may opt to go through dietary counseling sessions or seek psychiatric support due to their mental health issues, whereas some could decide to have these clinics beauty specialists for managing problems like acne resulting from high levels of male hormones known as Androgen.
Grace Women’s Hospital goes beyond merely treating patients by providing education on self-care so that its patients are informed about their condition. The goal is to provide comprehensive care and support for patients with PCOS, which will, in turn, enhance their quality of life and overall health status. This interdisciplinary group includes gynecologists, endocrinologists, nutritionists, and psychologists, among others.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can be detected through various signs and symptoms that may differ from one woman to another. There might be women who have little or no symptoms, while there are others whose signs are severe. Typical signs and symptoms of PCOS include:
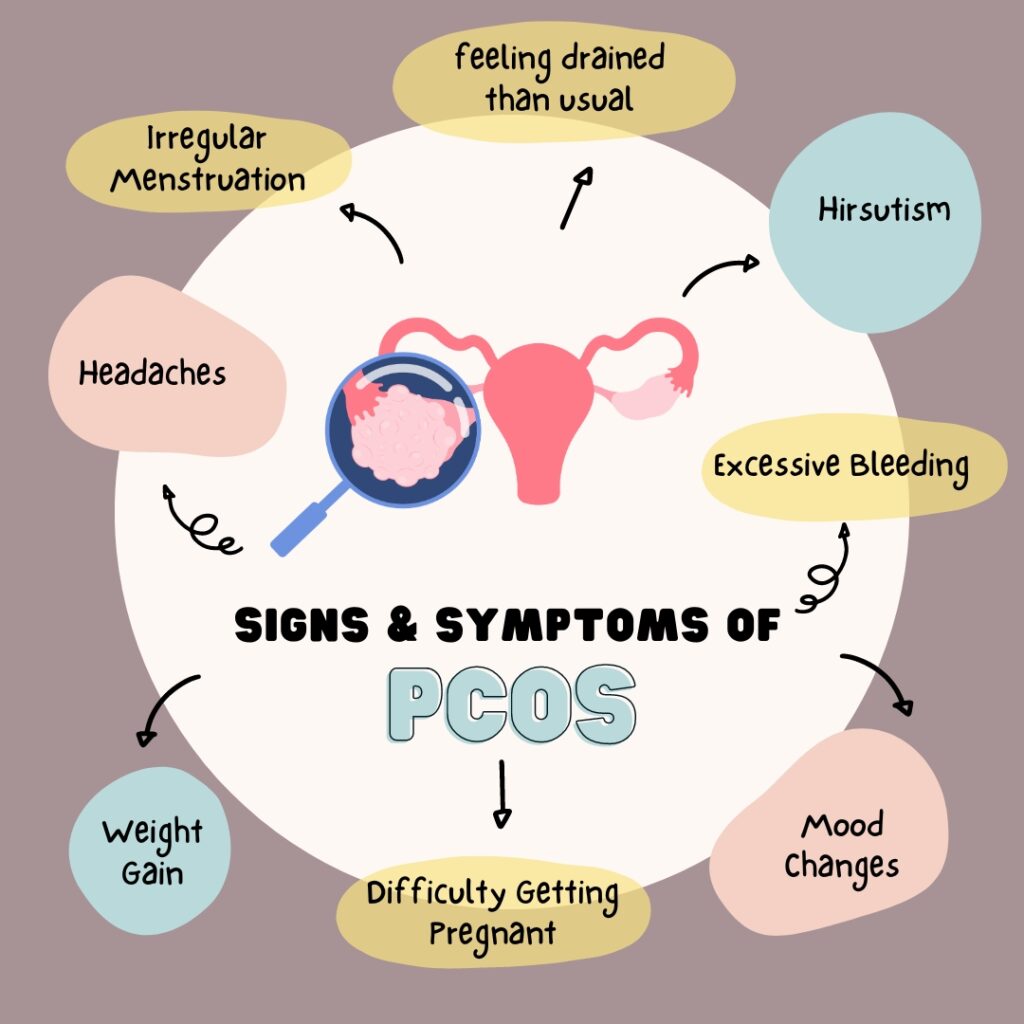
- Irregular Menstruation: It is a common symptom whereby those affected by PCOS have very few periods (less than eight each year) or irregular cycles with infrequent or too frequent menstruations.
- Excessive Bleeding: The reason why these periods may be heavier than ordinary arises from the fact that this uterine lining has been building up for longer durations of time.
- Hirsutism: This condition affects more than 70% of women with PCOS, causing them to have hair on their chin, chest as well as back. Excess male hormones cause hirsutism in these cases.
- Acne: With PCOS, skin becomes oily, leading to acne because a higher level of androgens makes the skin oilier than usual.
- Weight Gain: Over eighty percent (80%) of women suffering from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome are either overweight or obese. Mostly, it manifests itself through excessive deposition around the waistline, making carriers prone to complications related to obesity.
- Male-pattern Baldness: Hair on the scalp may become thinned out and start falling off.
- Darkening of the Skin: In body folds, for example, neck, groin, and under breasts, dark patches can be formed.
- Headaches: Headaches can be triggered in some women with PCOS by hormonal changes happening in their bodies.
- Fatigue: Women with PCOS often report feeling more tired than usual.
- Mood Changes: Like depression and anxiety too.
- Difficulty Getting Pregnant: Because of irregular ovulation or failure to ovulate, becoming pregnant can be difficult for women with PCOS.
Strategies to reduce the risk of PCOS
Managing weight is important as it can increase PCOS symptoms. The loss of some pounds improves symptoms, restore regular menstrual cycles and lowers insulin.
Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity and aids in weight control. Engaging in both aerobic activities and strength training would be beneficial.
Consuming whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains may assist in managing symptoms of PCOS. It is advisable to cut down on processed foods, sodas with added sugars as well as excess carbohydrates, which may lead to a spiking up in insulin levels.
Increased cortisol levels due to high-stress levels exacerbate the PCOS symptoms, thereby further impacting insulin sensitivity. Practice, like doing yoga or meditation for stress management, is good for us all.
Smoking tobacco increases androgen levels, which worsens the symptoms associated with PCOS. It is advisable to seek help in quitting Smoking.
Adequate sleep plays a key role in ensuring hormonal balance and management of PCOS symptoms. A person should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep every night.
Frequent visits to a healthcare provider will ensure monitoring of the symptoms, making adjustments in treatment plans if necessary, and screening any associated complications such as diabetes and high cholesterol linked with PCOS.
